Assembler Definition
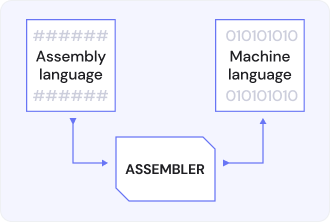
Assembler – is computer software processing the software, which receives instructions and translates them to the series of bits, on which the computer processor acts. The assemblers are programs which are in between the machine language which is understandable by the processor and memory of the computer and the language which is used by the assembly.
The type of assembler is associated with the number of times the program passes through the source code in the translation to the machine language. There are two major types of assemblers: Single-pass and Multipass. The next is the object code that assembler translates to from source code when compiled. The object code then gets written in the file in a sequence way in terms of number of bits that can be executed by processor. Some assemblers also supported object-oriented programming structures other than code translation to machine code.