Acceptance Testing Definition

Acceptance Testing is a QA activity intended to check if an application meets users’ expectations and, at the same time, the intended requirements. The consequence of an acceptance test is a pass or fail, which means that the software either meets the established criteria or has defects and problems that require fixing.
In some cases, depending on the QA methodology, acceptance testing might be conducted as beta testing, end-user testing, or application/field testing. The major goal of the acceptance test is to assist the development team in making sure the software is in line with the business goals and objectives, giving a clear indication of how much the final product corresponds to expectations.
The five types of acceptance testing
As we have mentioned in the previous section the types of testing for acceptance can be varied and respond to a specific amount of criteria and for the purpose of keeping it simple we will go over the five most widely used forms of this kind of testing method. Here is what they are:
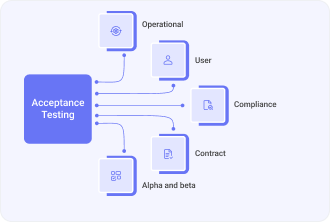
As we have mentioned in the previous section the types of testing for acceptance can be varied and respond to a specific amount of criteria and for the purpose of keeping it simple we will go over the five most widely used forms of this kind of testing method. Here is what they are:
- Operational acceptance testing is conducted with a goal of finding out whether the software is according to the requirements and therefore ready to be deployed.
- User acceptance testing as we talked about earlier is aimed at figuring out if the software is resonating with the needs of end users and ifit functions appropriately in real world scenarios.
- Compliance acceptance testing as the name implies is done for the reason of establishing if the final solution is in compliance with the local regulatory and legal compliances.
- Contract acceptance testing is similar to operational testing in some ways as it also is focused on getting to the bottom of whether the solution meets the expectations written out within the contractual agreement.
- Alpha and beta acceptance testing refer to the first part of conducting tests to find faults before the release of the software and the latter part is focused on getting the feedback from real users after the initial deployment.
Benefits of acceptance testing
Acceptance testing has a great value throughout and post-development stages, since it has a huge impact on user perception of the software. Early issue detection facilitates meeting quality standards, and therefore, product sealing, exactly as market expectations.
Also, it is worth mentioning that user acceptance testing, which is often time-consuming, can be a resource saver, and therefore, cost-reducing activity because discovering and eliminating bugs prior to release is many times faster and less expensive than post-release issue fixing.
This comprehensive method of acceptance testing not only increases product reliability but also leads to better user experience and a higher overall success rate for projects.
Tips for acceptance testing
As it is your moment to step up to the plate and show that solution actually meets end-users requirements and can face real-world challenges you definitely need tips that facilitate such a complex yet engaging process. Here are some of them from our middle and senior testers:
- Get time and prepare
You have to determine which aspects have to be tested so it is advisable to come up with essential data, user scenarios, and even make a checklist if you feel that there are many on the plate.
- Focus on real usage
It is not just a nice-to-conduct test but the one that is responsible for usability across every button coders and designers created, ensuring that it leads to the direct page and users will not spend time confused with what to click.
- Cooperate with other experts.
With any doubts for the core features, you can share your questions and feedback with those who made the software, work hand-in-hand with them to ensure it works well as it should be in the plan.
To summarize all being said keep your hand on the pulse of project and pay attention to minor inconveniences that may affect the user flow.