DMA Definition
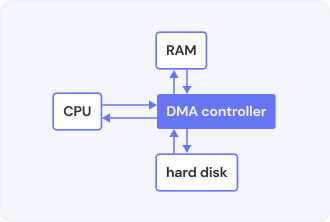
DMA (Direct Memory Access) — a computer architecture concept of input/output devices reading and writing data directly from/to the memory system without going through the CPU. Thus, systems can reduce performance load on the CPU for transportation of data to various parts; they can then smoothly be concentrated on other processing works via DMA.
On this operation, the CPU boots up, and the device sets transfer parameters before giving up control to the DMA controller. Data applications like backup processes, network communications, and graphic processing majorly use DMA in their high-speed transfer of data applications. This generally enhances system performance and efficiency as the data transfer leaves less overhead on the CPU. But DMA also raises the risk factors from the security point of view as well since it bypasses CPU-based protection memory allowing devices or software some vulnerability to it.