Calibration Definition
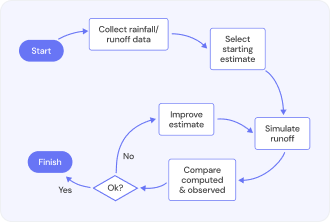
Calibration — a process of putting the output of the system into the comparison to the readings from a certain instrument or tool evaluating the result from an unbiased and accurate standpoint. Such a procedure helps in maintaining the correct operations of a device to keep it relative to an established and unchangeable standard.
It is a widely used method in software and hardware engineering for the sake of keeping the results of the outputs consistent and of high quality. The importance is further emphasized in manufacturing since it is playing a pivotal role that a tool is well calibrated for proper and secure functionality.
Purpose of calibration in software engineering
Calibration, engineering’s process of verifying measuring tools and machines, guarantees that they produce accurate and reliable results when referring to known reference standards. The process also corrects and identifies deviations, thus maintaining the same level of accuracy in manufacturing, testing, and quality control operations.
Regular calibration not only eliminates the possibility of expensive errors making it necessary to discard products but also keeps the company in line with industry regulations and safety measures. Also, it prolongs the life of the equipment by spotting wear or drift before major problems occur.
In the long run, calibration creates trust in measurement data, therefore, supporting enlightened decision-making and uniform product quality during the engineering processes.