ASCII Definition
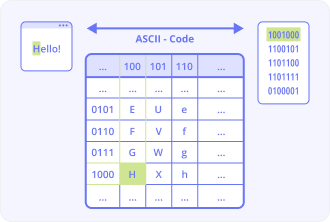
ASCII is an abbreviation of the American Standard Code for Information Interchange. Represented in the form of a text, it is the practice of data encoding used in electronic communications. The primary function of this method is to assign standard numeric values to all characters. That includes numbers, punctuation marks, alphabetical letters, etc. In this process, computers send data and establish communication with other computers, as well as keeping continuity while choosing the characters for textual information.
In ASCII, the Decimal character codes vary from 0 to 255 and 00 to FF in Hexadecimal. First defined in 1963 by the X3 committee of the ASA (American Standards Association), this practice is now widely recognized as a simplistic suggested standard way for communication based on text w
ASCII is an abbreviation of the American Standard Code for Information Interchange. Represented in the form of a text, it is the practice of data encoding used in electronic communications. The primary function of this method is to assign standard numeric values to all characters. That includes numbers, punctuation marks, alphabetical letters, etc. In this process, computers send data and establish communication with other computers, as well as keeping continuity while choosing the characters for textual information.
In ASCII, the Decimal character codes vary from 0 to 255 and 00 to FF in Hexadecimal. First defined in 1963 by the X3 committee of the ASA (American Standards Association), this practice is now widely recognized as a simplistic suggested standard way for communication based on text within software engineering.
ithin software engineering.