Boundary Value Analysis Definition
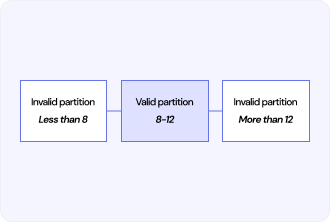
Boundary Value Analysis (BVA) – a reasonable path towards a range value boundary that is to be looked for in potential system-based error or vulnerabilities. Boundary values are criticality of BVA because the boundary conditions have been taken as the critical points in the software behavior where from the software can deviate from the normal path.
BVA allows for the deriving of the test cases in such a manner that all will have the individual boundary conditions. BVA, therefore, tries to find issues like off by one, inconsistency in relation to boundary, overflow or underflow through the testing in these critical points.
For instance, it would be the action of a software system taking within the range input values: BVA in this case would touch in tests that ensure the software system acts correctly should the inputs lie on the extremums, minimum, maximum, and boundary values of the said range.
The boundary value analysis is a process of immense utility to the software testers for recognizing and correcting the probable errors of great concern before these emerge within the course of real-life applications. It helps escalate the overall quality, reliability, and robustness of the software product.