Product Design Process: 10-Step Guide
You may wonder why there has been so much fuss about the importance of the product design process in 2024. The answer lies in the technological progress we witness today.
Some decades ago, product designers had limited access to data on market research, competitors, user research, user journey, usability testing, etc., that could help them with planning.
Nowadays, the situation has changed. Designers have plenty of tools, resources, and creative solutions that can be used in the design process. This article delivers a detailed explanation of each stage of the product design process and practical tips that can help you securely launch the project within the timeline and budget constraints.
What is the product design process?
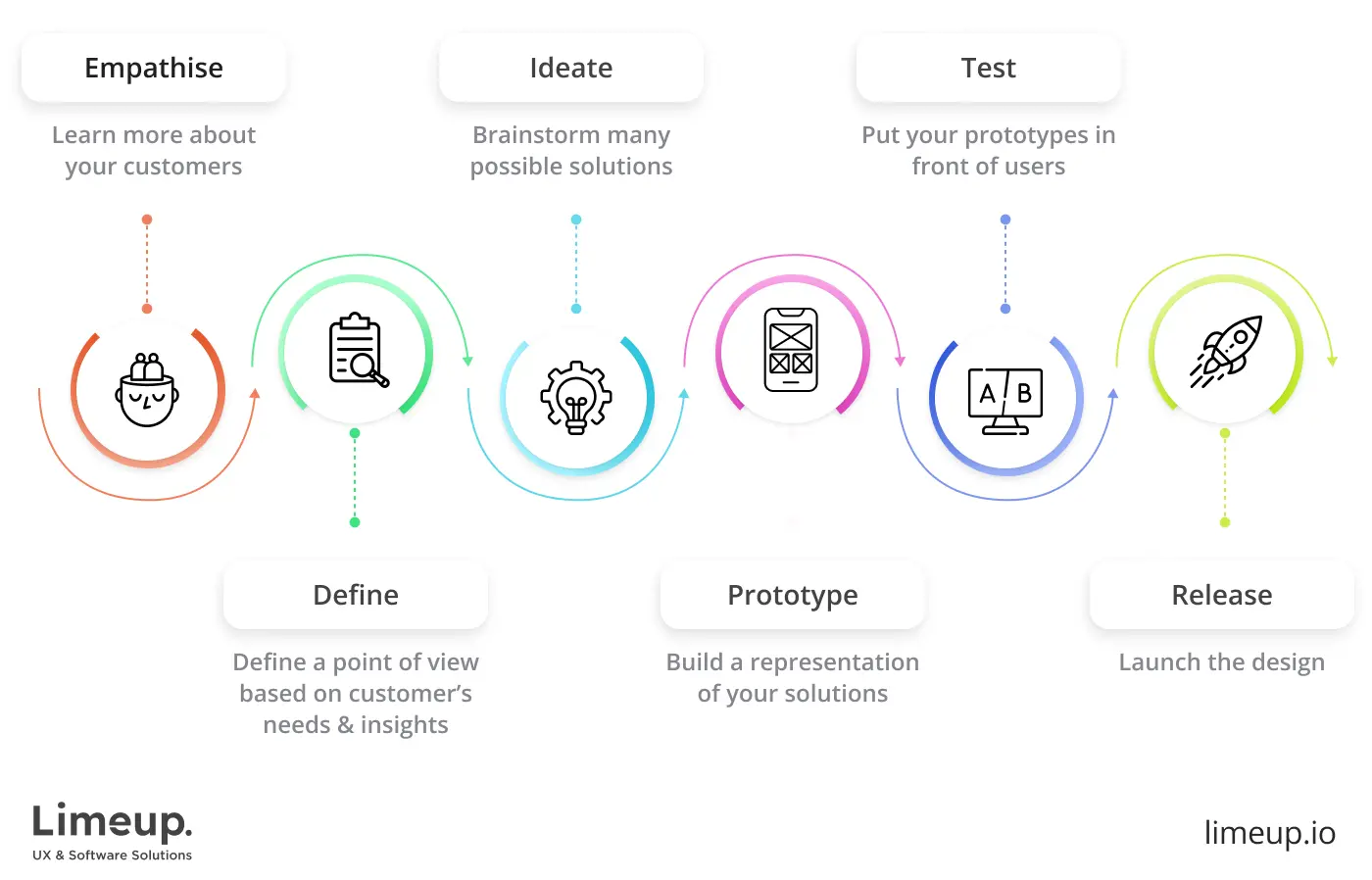
Product design process.
In 2022, the product design market reached $3 billion and involved more than 12,000 businesses making use of this service. The product design process stands for a step-by-step plan for allocating resources and designing an innovative solution. Its main components include inputs, methodology, limitations, and outputs.
The well-created product consists of the following elements:
- Appearance
- Features and functions
- Quality
To create a product that users will love, these 3 elements should be combined in a user-friendly and proper solution to client pains. Your product should be aesthetically appealing and visually attractive to your users. Also, it should be bug-free and performant as well as functional.
The team involved in the product design process performs many role-based tasks. The team members can include market analysts, marketers, product designers, UI/UX researchers, etc. Product designer has a lot of responsibilities, but their main mission is to plan out and create possible solutions that will satisfy user needs, user problems and provide a valuable user experience. They create products considering the market needs and trends as well as social and cultural conditions in which real users live.
So, the process of product design aims to help you catch a new market opportunity and implement it in a risk-free and effective way. In other words, it is a means of achieving your goal and converting an idea into a product step-by-step.
10 product design process steps
Below, we present a detailed guide that involves 10 steps. These steps can be changed, removed, or extended depending on your specific needs. They are not mandatory to complete, but they offer guidance to rely on when designing your own product strategy.
1. Brainstorming
Brainstorming, also known as the ideation phase. It involves generating creative ideas around the future product. You can organize brainstorming sessions with your team or conduct brainstorming by yourself.
Typically, brainstorming consists of 3 phases. The first phase is the problem statement. It lies in defining the user problem a product is expected to solve. Next, you will generate ideas on the ways in which the user’s pain can be solved. The problem-solving phase requires you and your product team to be creative and responsive. If your team is overloaded with daily tasks and duties, they might not have enough inner resources to participate in brainstorming. Therefore, you should allow the team to devote some part of their work time to the process and make sure that they are interested in the end result.
The final phase of brainstorming is to prioritize creative ideas and select the most relevant ones. For this, you may also need the help of your employees. Ask them to share their life experience in solving similar problems as being in the customer’s shows.
During this stage, the idea of quantity is more important than quality. You should collect as many ideas as possible. Sometimes, a pretty absurd idea can lead you to the thought of a unique and truly competitive product. So, at this stage, give your employees enough freedom to express everything that comes to their heads. Do not criticize their ideas and demonstrate your readiness to go out of the borders together with your teammates.
How to make the process more effective?
We have an idea for you on how to make brainstorming more effective when organizing group sessions. Voice a client pain you want to solve in your product and subdivide your design team into two groups. Each team will have their own task. In the first group, the team members brainstorm creative ideas for a product. The task of the other team is to process, evaluate, and improve these design ideas.
Give each team enough time to complete their task — it can be a day or a few. Ask them to present their ideas in any way possible — via drawings, schemes, bullet points, stories, etc. To encourage the team members to be more active, offer them some kind of reward. Hereafter, organize a workshop where you will be involved in discussing ideas, selecting the best ones, and coming up with the best suggestion for the product.
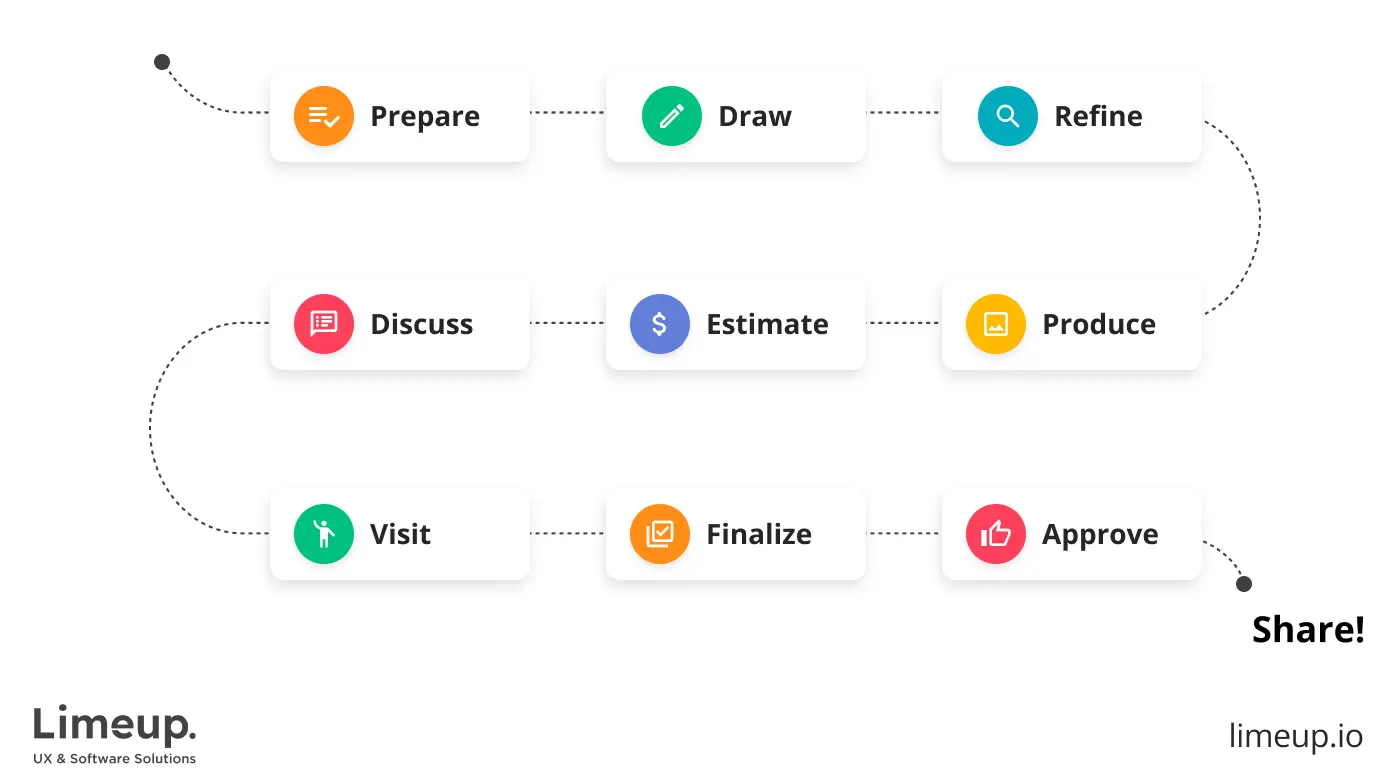
The 10 step solution of the design process.
2. Developing a product vision
Developing a product vision requires you to choose viable ideas from your list and establish the foundation for a product design process. At this stage, your ideas should turn from general and abstract to specific and clear.
In other words, product vision will help you set the direction for your project. At the same time, this stage is not about setting clear deadlines yet.
When developing a design thinking methodology, you are going to validate your assumptions and frame the users’ problems to be solved with the product. The exit criteria for this stage is the statement of the problem describing the pain points of the target user and the way they will be satisfied with your product.
Using this information, you will be able to develop clear, achievable, and measurable project goals that will form the ground of your project KPIs and success criteria. Also, at this stage, you should consider the risks and challenges that may occur on your way. Product design companies in the UK implement a complex process for creating the right product vision that will reflect your brand, help you minimize risks, and bring innovation to the market.
To create an effective minimum viable product, a product designer has to answer the following questions:
What is your product’s main goal?
You may answer that your goal is to create an app or a website. However, building an app is not the best example of a goal as it lacks specification. You should try to define the goal precisely and outline the main function your solution will perform. For example, “I will build an app that helps users learn foreign languages in an interactive way” or “I will create a website where people can promote and offer their services.”
How are you going to achieve this goal?
Think about the means, tools, and resources that will be used in the product design process. A product idea may be relevant and viable, but it loses its chances for business success if it is unattainable. To prevent this from happening, you should make sure that you have enough resources to develop an effective thinking approach.
Who is your target user?
Focus on the target audience of your product here. The audience should benefit from your product. Otherwise, they won’t use it. Try to outline the distinctive characteristics of the product that will encourage potential users to choose you over competitors.

Analyzing your target audience.
Why do you want to create such a product?
When answering, think about the product from the user’s perspective. You should clearly see how a product will make your user’s life better and what value it will bring. The answer to this question will form the ground for developing your brand identity and culture at the stage of product promotion.
Overall, your product should have a purpose, and it should lie not only in making a profit. Seeling money as a primary target shifts the focus from the target user to your desires. This will make it harder for you to earn the client’s trust and attract their attention to your innovative solution.
As you see, there is a lot of food for thought at this stage of product creation. Try to keep the information short and clear. As you will include it in your project documentation and use it as a basis for further product design steps, it will be more convenient for you if it is presented in a laconic way.
3. Product research phase
Each assumption you make in the previous steps should be proved by facts, statistics, numbers, trends, etc. In other words, this step requires you to apply a data-driven approach to collecting information.
During the product research phase, your product team will conduct a detailed overview of the market you expect to enter, competitors offering similar digital products, target users, etc. Also, you will evaluate the product longevity by checking the trends for the upcoming years and reviewing market statistics on the chosen niche. Try to delegate the critical responsibilities of this step to employees who specialize in research. For example, market analysts or business consultants.
Here are the main types of research that can be leveraged at this step of the design methodology:
Surveys
Surveys are helpful at nearly every stage of your idea realization. Surveys and questionnaires enable you to get a lot of useful information about a product and its potential. One of the benefits of surveys is that you can formulate the questions in a way you wish and get precise answers to your concerns.
Remember that at this stage, your audience is not as interested in growing your product as you do. They do not understand the value it can bring yet. Your audience will not be eager to dedicate much time to a survey. Thus, when preparing questions for a survey, try to stay clear and laconic.
Also, avoid asking questions that presuppose binary, biased, or vague answers. Do not include questions that may be misinterpreted. The good idea is to combine short questions with yes/no answers with open-ended questions that require an extended answer.
A survey provides valuable insights and data from the target audience.
Stakeholder interviews
Interviews with stakeholders can provide you with a broader look at the process of product design. Unlike surveys that presume limited answers, interviews give you a chance to get detailed explanations, take control of the communication flow, and lead the conversation.
The best way to perform stakeholder interviews is to organize face-to-face meetings. Before starting a conversation, a stakeholder should be informed about the purpose of the meeting and its impact on the project. The conversation should take place in comfortable conditions.
When having a conversation, pay attention to the non-verbal signs. For example, when a stakeholder says that they agree with the position but their body language reveals the opposite. To avoid such situations, try to make sure that the conversation is unbiased. Explain the purpose of an interview and note that the answers won’t affect the person’s status and position in the company.
Field studies
Field study is collecting raw data on a specific topic. For instance, you can conduct user stories about the study on user behavior, target niche, interaction with your product, etc. The main difference between field studies and other competitive research types is that a field study makes you integrate into the natural environment and study them instead of reproducing these conditions artificially.
Field study enables you to sport the correlation between different aspects and factors. Namely, when conducting a user-focused field study, you may spot the peculiarities of user interaction with a product, specific needs that satisfy with technology, pain points that are not covered with creative solutions yet, etc. With the help of this domain research type, you will know the context from the inside out.
Market analysis
A market analysis focuses on researching the conditions (social, economic, cultural, etc.) in which your product will exist. If you use only trusted resources, this crucial component of product creation can be very insightful for your future.
When studying the market, focus on the following aspects: product demand, market size and share, economic indicators, demographics situation, market saturation, and pricing. Also, the research may involve an overview of market trends, which will help you keep pace with market news and innovations.
Competitor analysis
You may wonder what the difference between market research and competitor analysis is. Market analysis helps you define the circumstances and the context in which a product exists. Meanwhile, competitor analysis helps you define the features or characteristics of your product that will give you a competitive advantage.
Diving into the subtleties of your competitor’s business, you will better see your strong and weak sides. This information can be used to define the unique value that the customers will get if choosing your product.
User research
The process cannot be effective without user research. This type of research allows you to study your target audience in-depth and literally puts you into your client’s shoes.
To complete the research, collect qualitative data on the needs, pains, interests, preferences, etc., of your audience. For this, you can involve various research methods, from passively observing the user behavior to involving them in the interaction with your product or products alike.
When conducting the research, focus on data that answers the following questions:
- What does your audience think about the product?
- What feelings do they have throughout the user journey?
- What do users say about the product or similar products?
Keep in mind that there may be a difference between how you imagine your user and what they look like in reality. Striving at the ideal image of your client may lead to the fact that you develop a fake product vision. This is why user analysis should be focused on real-world data only.

Creating User Persona will help to see a collective image of target users.
User and market research
To summarize the previous product research phases, you have to pay particular attention to researching the target audience in the specific market in which the product will be introduced.
Having a comprehensive understanding of how the users in a certain market interact with the product, as well as what their expectations and goals are, can help deliver a product that actually solves their problems.
So, it’s best to analyze users and the market that you’re targeting collectively. That way, the data you gather will be more consistent and nuanced, increasing the likelihood of building a successful product.
4. Conceptualization
Conceptualizing your product idea involves seeing a solution as a basic idea that you fully grasp. You have the answer to the questions like “What user needs will a product cover?” or “What effect will a product have on the target audience?” or “How to reach potential users and tell them about a product?”
By performing conceptualization, experienced product design companies pave the way to the next stages, where they collect requirements, wireframe the idea, and create prototypes.
User journey
In essence, the user journey encapsulates mapping out the steps that the user takes, from initial interactions to completion of the task. You have to build a comprehensive journey to understand what the user’s thoughts and feelings are while interacting with the product.
Identifying all interaction points throughout the journey can help create an enjoyable and smooth experience. For example, an interaction point can include the user clicking certain buttons, navigating through screens, filling out forms, etc. By conceptualizing the actions that the user will take, you can meet and satisfy the user’s expectations.
5. Collecting requirements
This step in the process of product design involves making a list of requirements and product specifications.
Using the data from user research and other studies, you will compile both the project and product requirements. Project requirements include estimating the cost, timeline, and team composition needed for creating a successful product. Describe all of these in the project documentation and share them with the team.
Typically, the project itself is broken down into smaller phases. Each phase of the linear steps is dedicated to a particular milestone, with responsibilities and tasks outlined. It’s highly recommended to involve the help of a product manager and stakeholders at the step of collecting requirements. Together, you will estimate the approximate milestone duration and the amount of resources needed for implementing an effective product design process.
Meanwhile, product requirements include the description of the product structure, features, and functions. To make the product requirement list, refer to your target persona. Ask product designers to conduct user journey mapping. The result should provide you with a detailed description of the user flow and the actions users should perform to achieve a goal.
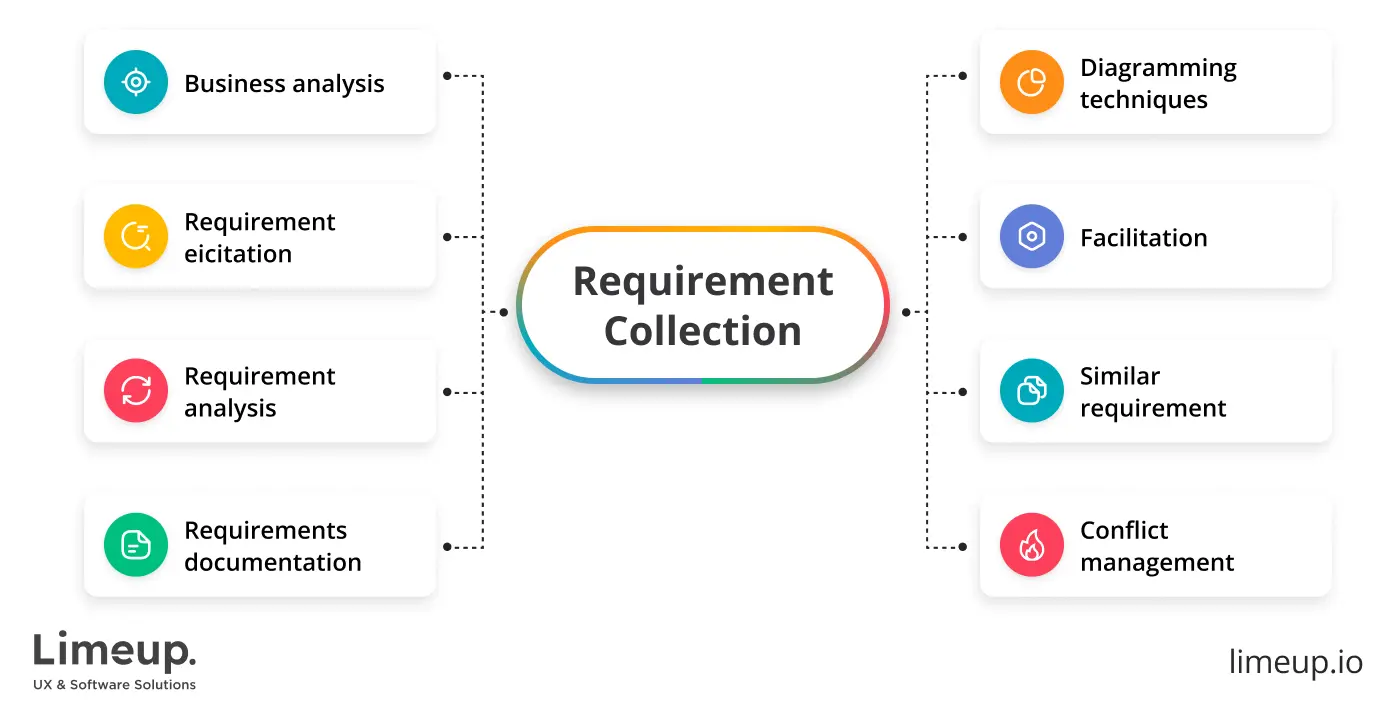
Requirements collection.
6. Prototyping
At this step, we move from conceptualization to creating reliable and realistic representations of a product. The difference between conceptualization and prototyping/wireframing lies in the fact that conceptualization is more basic. It just answers the question of what kind of object/solution/product will be built. At the same time, wireframing and prototyping answer the question of what a product will look like and what features it will have.
Prototypes are like the skeletons of products and their functions. They help you grasp the information architecture of your future solution. Product design companies in London are known for their ability to complete prototypes quickly and according to the requirements. By creating a prototype with the help of prototyping tools, the companies can prevent many errors, which will save you time, effort, and money.
We can differentiate between low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes. Low-fidelity prototypes are very general and basically illustrate a product. Meanwhile, a high-fidelity prototype takes more time to create but offers a more detailed look at a product design and its features.
7. Testing
This step is essential for making sure that your process coincides with how your users see the product. At the user testing stage, you can collect user feedback or organize user interviews after they interact with a product. With the help of testing, you can fix mistakes that may affect user perception of the product.
Usability testing is taking your target users into controlled and observable conditions where users interact with your product. It can be as follows: you ask your users to achieve a certain goal with the solution. Then, you collect information on the user flow and the actions they take to achieve it. With its help, you can detect core usability problems and fix them promptly.
When conducting usability testing, pay attention to the following:
- Aim I right with the choice of the target audience?
- Have users faced any difficulties throughout the user journey mapping?
- What kind of experience does your product offer to the user?
- Can you simplify the user’s path to achieving a specific goal? How can I do this?
If there is any opportunity to shorten the user path to a certain goal, use it. Your audience will appreciate the experience if the user journey map is efficient.
During this stage of the design development, it’s also important to record sessions either face-to-face or remotely. By having a session recording, you will be able to return to the aspects that require careful analysis.
How many users should be involved in usability testing?
When planning user testing, you may wonder how many people should be involved in the sessions. The more, the better is not the best approach here. In the article by Jeff Sauro, the author presents precise calculations on this matter.
According to Sauro, the overall probability of facing usability problems when using a solution is around 31%. As the rule of binormal probability reveals, if you involve five users in testing, you increase the chances of spotting usability issues by up to 85%. Meanwhile, if you decide to involve more users, you will keep detecting the same issues that the first five users spotted.
So, you don’t need a lot of users to detect the usability issues, users’ problems and fix them before your product goes live. Of course, this number also depends on the scale of your product, your business peculiarities, the peculiarities of buyer persona, etc. However, by having around five users involved in testing, you have a lot of chances to detect the most crucial usability issues and get rid of them promptly.
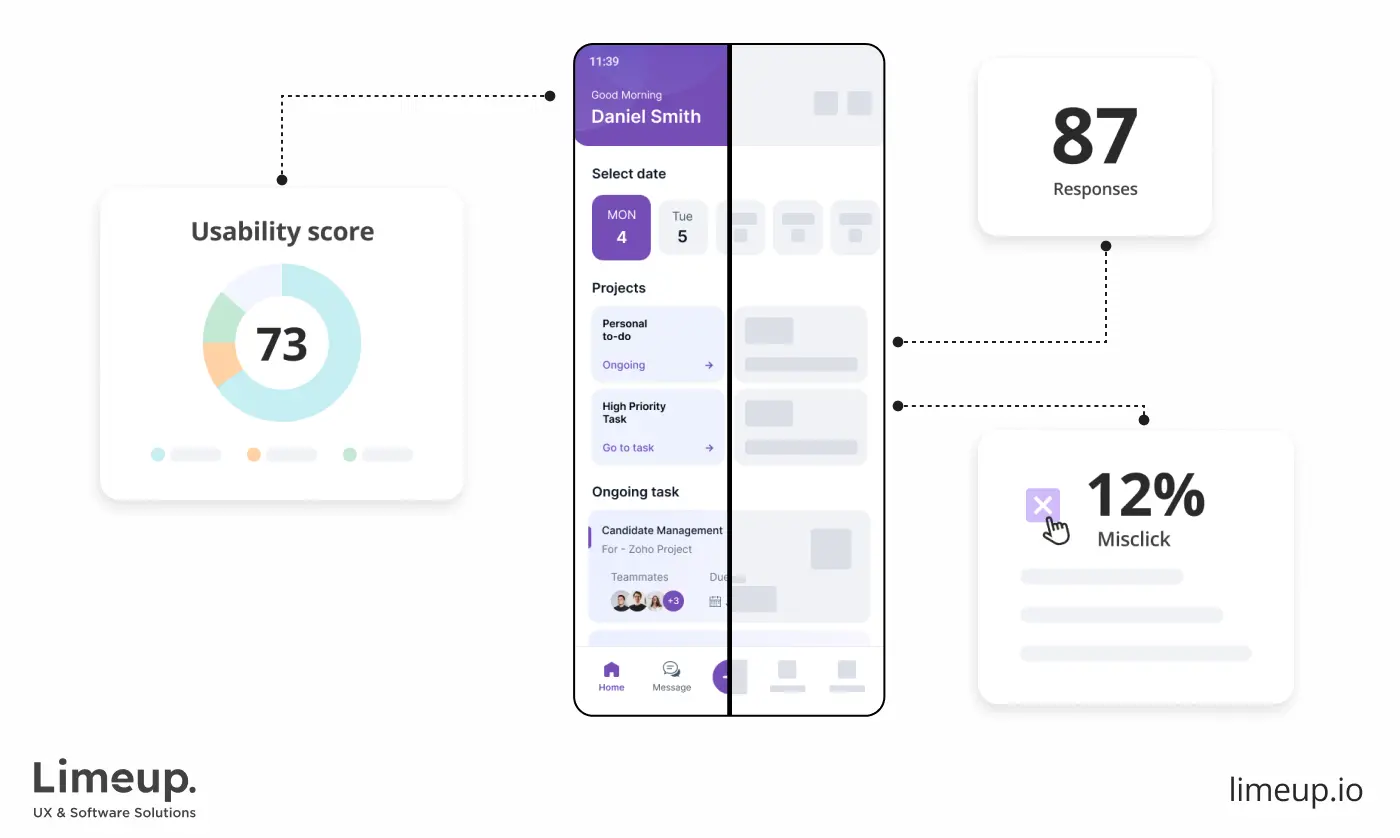
A usability test helps identify usability issues and provides actionable feedback.
8. Iteration and validation
The next step in the product design process is iteration. Before moving to full-scale product design, you should improve the prototype with the help of prototyping tools. Iteration based on stakeholder and user interviews as well as user research.
It frequently turns out that one complicated aspect of the user journey leads to difficulties and challenges in other aspects. It is possible solutions will cost you more to return to the redesign after the product release. Therefore, do not underestimate even the minor usability issues, as they can have a direct impact on the product’s popularity and your profit accordingly. Try to master the prototype before starting the product creation.
9. UI/UX Design
UI/UX design is creating a design system and a full-scale product design by leveraging convenient tools and insights from the previous steps.
If you choose the agile approach, the design iterations will be subdivided into sprints. Sprints usually last for 1-2 weeks and are dedicated to a certain part of a project. Effective project management will enable your teams to work in parallel, which will improve productivity and speed up task competition.
Apart from creating the design itself, you will also be required to create a design system and UI kits. Design systems are a set of design standards and reusable components that make up the product’s essence. Meanwhile, a UI kit is a set consisting of UI components and design patterns (fonts, colors, icon styles, design files, other UI elements, etc.) that represent your product’s visual look.
10. Quality assurance
After the product is released, collect user feedback or conduct user interviews and analyze the data. To encourage your audience to leave feedback, offer them some kind of reward. For example, after evaluating a product, they can unlock a special feature or earn some additional points or a higher level.
You should keep product quality in mind at every step of the product design process. Even if you tested a product thoroughly, some drawbacks might show up only after it goes live. Thus, it is vital to find a company offering product design services that end with ongoing support and maintenance.
The advantages of following a product design process
Here are the main benefits you get if you follow effective product design stages:
Stick to the budget and timeline
Well-analyzed design iterations help businesses stick to the budget and such a layout timeline that was estimated at the beginning. Here, the stage of planning and collecting business requirements is essential. During this step, a project manager estimates how many resources will be needed to build a product. They clearly define the design project scope, which gives businesses a better understanding of the expenses and project duration.
By following the product design techniques, your team will be involved in iteration phases. During each phase, you will make an overview of the project accomplishments, challenges, or issues. This, in turn, will help you prepare a response strategy and prevent delays or failures.
Planning the budget & timeline clarifies the workflow.
Set measurable goals
Having a great product idea is a big journey. Each step can be dedicated to a certain goal. It’s important to make each goal achievable, measurable, and precise.
By planning the product creation, you will see the clear connection between the product requirements and the results that fulfill these requirements. Insights and user experience you gain at each step of product creation will serve as clues on your way to creating products.
Get a quality product
Quality control and user acceptance testing will help the product team adjust the concept to the market standards and user expectations. Similarly, post-design usability tests and continual product improvement after the release will help you make sure that your solution is up and running. Later, if you hire a product designer, they make sure that the product quality match with high design standards.
Prevent risks
When planning a product design process, you get the chance to put your product into context. During this step, you study the market circumstances, the audience’s readiness to accept the product, the capabilities of your business, etc. By collecting all this data, you also get the knowledge of the possible risks and challenges that may occur on your way. In this regard, an effective risk management strategy can be a good addition to your main strategy.
Know what your users want
The last stage is quality assurance, which lies in ongoing support and maintenance. At this stage, you can collect data, leverage various data analytics tools, visualize your insights, and draw conclusions on the product’s performance.
The numbers you collect will tell you a lot about the client’s attitude to your product and the difficulties they face, if any. With the help of this data and client feedback, you can improve the product and shape the user experience that your audience seeks.
Ensure effective teamwork (everyone is on the same page)
According to the agile methodology, the project can be broken down into multiple phases. The work during each phase is organized in a way that different team members can work on their tasks in parallel.
In this context, well-documented design steps are a kind of instruction the team can refer to anytime. It will serve as a guide that gives them a better understanding of the requirements at any given stage.
Prioritize tasks
Going through all the product design process steps will help you create a precise product vision with a list of features, characteristics, and attributes. You will be able to group the features by importance based on the data you get from the user research. This will result in prioritizing tasks that are vital for your product’s performance, usability, and security.
Conclusion on implementing the product design process
In this article, Limeup’s team answered the question, “What is the product design process?”. We based this guide on field knowledge, practical experience, and a deep understanding of the market, with brainstorming and finishing with maintaining quality and supporting a solution.
As design experts, we can hardly overestimate the benefits a well-planned process can give. Generally speaking, its purpose is to bring clarity and organize the work in the most effective way possible. If you have any questions left, our team will be happy to share our vision and experience with you and sort out all the details.









